Joern can be enhanced via plugins. Plugins can…
- … access the code property graph using the query language and create new nodes, edges and properties via the DiffGraph API.
- … interface with arbitrary Java libraries to e.g., access the filesystem or network, or data analysis capabilities.
- … add new node and edge types to the schema, or extend definitions of existing node and edge types
In the simplest case, plugins add queries to Joern, as for example the
query-database plugin does.
Managing plugins #
Plugins are distributed as zip files containing Java archives. They can be written in any JVM-based language, e.g., in Java, Scala, or Kotlin.
Joern comes with a few plugins pre-installed. You can list installed plugins using
joern --plugins
New plugins can be added:
joern --add-plugin <zipfile>
and removed:
joern --remove-plugin <name>
You can download an example plugin here for testing:
https://github.com/joernio/joern/releases/download/latest/querydb.zip
Developing your own plugin #
We provide a sample plugin written in Scala that you can use as a template. In order to build it yourself, make sure you have the following dependencies installed:
- OpenJDK 19 or higher
- sbt (any version)
You can then install and test the sample plugin by running
git clone https://github.com/joernio/sample-plugin.git
cd sample-plugin
./install.sh
This will install joern in the sub directory joern-inst and create
symbolic links in the working directory. Finally, it will add the sample
plugin to the aforementioned joern installation via joern --add-plugin.
Now start joern:
./joern
and on the joern shell, type
run
You should see the sample plugin named gitextension in the overview
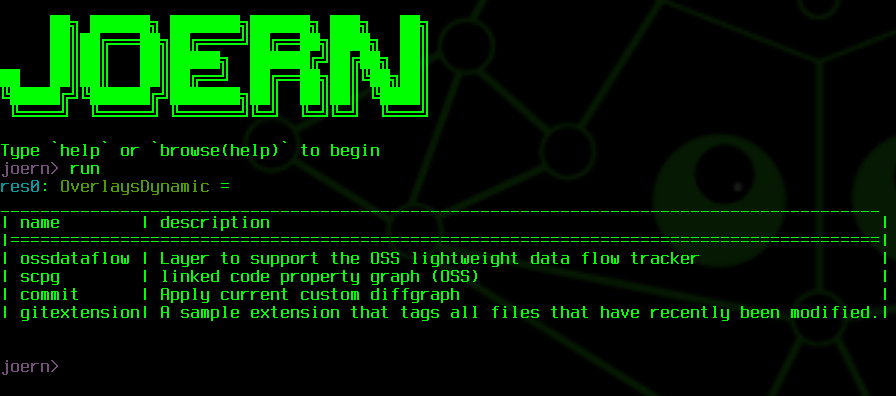
You can inspect and modify the options of the example plugin via
opts.gitextension.<TAB>
To run the extension on the shell, type run.gitextension. This should
throw an exception, indicating that no projects are loaded.
Importing into the IntelliJ IDE and running tests #
Joern plugins can be developed in an IDE and the process of importing a plugin may differ slightly from IDE to IDE. The following instructions are for IntelliJ 2020.1.1.
Choose “Open or Import” to import the project.

Next, select the directory from the file selector. Assuming that your
IntelliJ installation has support for sbt installed, the import is
fully automated.
Finally, navigate to src/test/scala/io/shiftleft/gitextension and
click on GitextentionTests. You can right-click on the class or the
individual tests to run them.
Building a shippable plugin #
You can create a plugin ready for installation via ./joern --add-plugin by
running:
sbt createDistribution
Adding dependencies #
You can add dependencies by modifying the variable
libraryDependencies in build.sbt:
// build.sbt
name := "joern-sample-extension"
ThisBuild/organization := "io.joern"
ThisBuild/scalaVersion := "2.13.0"
...
libraryDependencies ++= Seq(
// Add your dependencies here
"org.eclipse.jgit" % "org.eclipse.jgit" % "5.7.0.202003110725-r",
// ...
"org.scalatest" %% "scalatest" % "3.1.1" % Test
)
...
Extending the CPG schema #
In order to extend the Code Property Graph schema specification in your
plugin, use the codepropertygraph-schema and overflowdb-codegen packages
in your build files, together with an extension of the original schema which
defines what will be extended. The sample-plugin contains a working example
of the usage of the aforementioned packages in schema/build.sbt, and an example
of the schema definition at schema/src/main/scala/CpgExtSchema.scala.
The example schema extension only adds a new node type EXAMPLE_NODE and a new property EXAMPLE_PROPERTY. The new property is added to both the new node type as well as an existing node type from the base schema.
// schema/src/main/scala/CpgExtSchema.scala
val exampleProperty = builder.addProperty(
name = "EXAMPLE_PROPERTY",
valueType = ValueTypes.STRING,
cardinality = Cardinality.ZeroOrOne,
comment = "an example property")
val exampleNode = builder.addNodeType(
name = "EXAMPLE_NODE",
comment = "an example node"
).addProperties(exampleProperty)
cpgSchema.base.file.addProperties(exampleProperty)
The schema is defined in overflowdb-schema, which is a Scala DSL. I.e. you can open sample-plugin in your favorite IDE (we recommend IntelliJ IDEA) and get autocompletion, compiler feedback etc., which should help with creating your schema extension. For more inspiration you could explore the base cpg schema definition which is split across multiple files for modularity: https://github.com/ShiftLeftSecurity/codepropertygraph/tree/master/schema/src/main/scala/io/shiftleft/codepropertygraph/schema
To generate the domain classes and install the schema extension in your joern distribution (must be installed first), simply run ./install.sh in the sample-plugin.